
Work Order Management: Definition, Importance & Best Practices
In modern facility management, tasks are assigned as work orders. The latest CMMS (computerized maintenance management system) solutions in the industry, along with Digital Twins, enable preventive scheduling and maintenance. All these further contribute to work order management practices in large facilities in the US. Stats from the Global Growth Insights say nearly 65% of organizations are using CMMS to structure their work orders, track, and execute better. This allows managers to assign tasks to technicians based on various parameters that support enhanced productivity and efficiency. There are preventive maintenance work orders, which are used to schedule routine servicing for all of your equipment.
What is a Work Order?
Every task assigned to a technician, whether it is to perform maintenance, repair, or inspection, is documented in the system as a work order.
Work orders provide valuable insights to facility managers, including task details, assigned personnel name, resources utilized, location, and scheduling.
These are essential for an organization’s maintenance strategy to track progress and organize maintenance activities with greater control, driven by accurate data.
Now, as new features and capabilities are getting added to the premium Digital Twin-integrated CMMS system, work orders cannot be of a single type.
For example, in large semiconductor or industrial facilities, there are intricate machineries that need to be monitored and maintained, to keep operations smooth, as downtime would cost thousands and sometimes millions of dollars.
So, here are the types of work orders.
Types of Work Orders

Depending on the organization’s size and the industry it operates in, the work order prevalence changes. For instance, a semiconductor facility will generate a higher volume of routine cleaning-related work orders due to its processes that are vulnerable to microscopic contamination.
Compared to this, a hazardous chemicals manufacturing company will require more safety-related work orders. Hence, the understanding of the following eight types of work orders is essential before handling them.
- Corrective maintenance work orders
- Electrical work orders
- Emergency work orders
- General work orders
- Inspection work orders
- Preventive maintenance work orders
- Safety work orders
- Special project work orders
Corrective Maintenance Work Orders
These types of work orders are typically associated with routine inspections from technicians and are part of reactive maintenance. It helps organizations from various industries address issues that may generate downtime downstream. During an inspection, a technician uses various tools and their experience to find issues in equipment or specific equipment parts of existing systems. Once the assessment is done, corrective maintenance work orders are generated to either fix the parts or replace the equipment. However, these are different from emergency work orders. Emergency work orders are created in response to an unexpected breakdown.
Electrical Work Order
These are tasks assigned to repair or install electrical equipment, including lighting, power supplies, sockets, and all other electrical appliances.
General Work Order
General work orders are those nonurgent tasks, including pest control, painting, minor carpentry, and signage installation, etc. These are low-risk tasks and hence do not fit into a more specific category. Such tasks are common in commercial, hospital, and healthcare facilities.
Inspection Work Order
These types of work orders are more common in facilities that practice predictive or routine preventive maintenance. When there are inspections needed as part of the structure of such type of maintenance, a series of tests is performed.
Renowned CMMS solutions have the ability to provide detailed test series for each equipment to technicians. Inception work orders help identify anomalies, risks, and provide detailed insights into asset performance and other functionality issues.
Preventive Maintenance Work Orders
These are the scheduled work orders for different equipment, aiming to maintain their functionality optimally. These work orders are also focused on extending equipment lifetime, with customized scheduling of preventive maintenance tasks
Organizations looking forward to decreasing downtime, maintaining regulatory compliance, and cutting down maintenance or technician expenses, understanding preventive work orders is a must.
Safety Work Orders
These orders are solely focused on worker safety, including any equipment malfunctioning, and in high-risk environments, safety work orders are the sole focus of some firms.
People working with high-risk equipment or who need to maintain a safe distance from a certain area, safety work orders create structured tasks that ensure these areas are maintained.
Special Project Work Orders
These work orders are related to the projects undertaken to modernize and advance facilities. It includes installing new equipment for extended services, increasing resources for more productivity, etc.
We mentioned earlier in this blog about the work orders being documented with their details. But there is a process specific to every industry that defines how work orders are requested, performed, and documented.
The Work Order Process
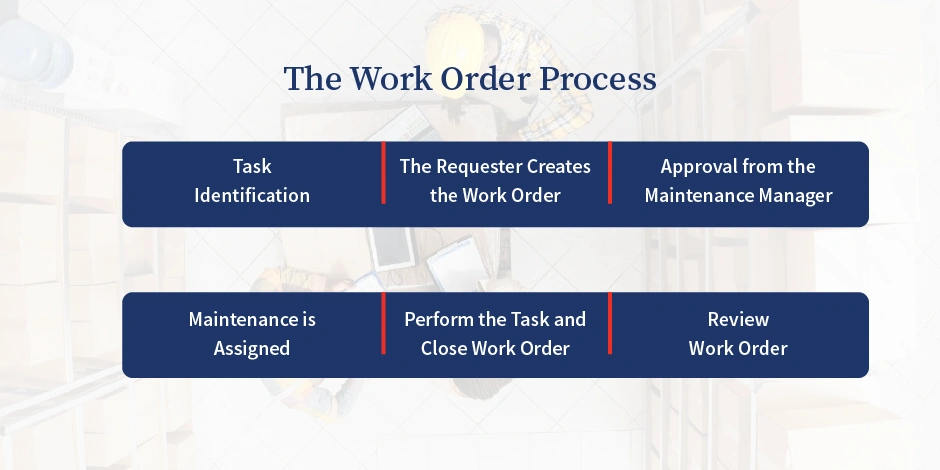
The work order is the fundamental element of the maintenance data, based on which further things are calculated. The work order document becomes the primary mode of communication and documentation of the method.
Task identification
This is very natural in every process, whether an organization is installing a CMMS software or assigning work orders. The first step is to identify that there is a requirement for work to be done. Now, this can be prompted in several ways. There are malfunctions to be noticed in time-based usage and usage-based cues. Facilities that use IoT sensors’ real time data for monitoring get notifications from the CMMS system itself that a task has to be performed.
It indicates the equipment, the location, and the available technicians to be assigned. If there are multiple notifications generated, the system also mentions the priority of the tasks.
The requester creates the work order
Now, the requester receives the work order details from the system and creates the basic form of the work orders. The basic information included, the location of the asset, the issue/maintenance task required, details about the situation, photographs and videos if applicable, and any other important information. Today’s system, with IoT sensors and Digital Twin integration, provides more detailed and accurate responses for smooth tasks.
Approval from the Maintenance Manager
The next step that immediately comes is to approve the request. This step is mandatory because it filters unnecessary work orders from inexperienced requesters before submitting work requests. There are several cases when work order notifications are interpreted falsely.
If the maintenance manager finds any discrepancies, they send back the requests to the requester for reanalysis. Also, the other way happens when there are any requests for special parts or tools from the spare parts inventory management. The maintenance manager is the authority who will approve that specific part or tool request in this step and also elevate asset management practices.
Maintenance is Assigned
In today’s CMMS systems, maintenance is assigned automatically through the system. However, if that is not set up in your organization, the work order needs to be assigned manually. The automated system is more intelligent in determining the following factors:
- Urgency
- Readiness of the team/current workload
- Overall impact of the issue
- Available technician’s skillset
In case of manual assignments, the relevant authority has to consider the above factors before assigning the maintenance task.
Perform the Task and Close Work Order
Once the work is assigned, the technician gets a notification on their phone through the CMMS mobile version. CMMS mobile apps make it easy for field technicians to access manuals and update statuses on-site, improving efficiency.
CMMS on mobile devices also enhances field access and control, which is why around 52% of users now manage tasks via mobile devices, says Industry Research.
The installed application shows them an easy interface with all the details and some options. These options indicate whether the work is accepted and started by the technician, and if there are multiple sub-work orders under one, there are also options to mark them closed for each.
The Seventh Edition State of Service Report, by Salesforce, shows enhancements in customer expectations as per 74% of mobile workers.
Also, if required, once the maintenance work is finished, technicians can upload photos and other details to document their work. The details include the time spent on performing maintenance, resources purchased, and images purchased or videos. In modern CMMS, digital trails automatically record maintenance actions with timestamps, aiding in compliance during audits.
Review Work Order
This is the last step, when the technician closes the work orders, and the maintenance manager is notified about that. He checks the status for quality assurance, and the work order stops periodically, with the asset going back to its normal operational state. The asset continues to function until another issue arises, and the work order process restarts for continuous improvement.
Since the start of the process, when the basic work order is created, the data and its accuracy become a fundamental factor for the whole process to progress smoothly. Organizations need to understand the details required in a work order to fully automate the process, ensure transparency, and effectiveness of the process.
So, here is a detailed look at the details required for the work order for that effective communicator.
Information Should a Work Include
The information in a work order management software should not be vague; rather, it must contain clear action steps. In order to get the work order successfully closed, all the necessary details should be accurate and well-structured. The work order management software increases data access by centralizing work order information, allowing technician members to track and edit tasks in real time. Not only should it guide the technicians, but also become valuable data for compliance, accountability, and long-term asset maintenance through the work order management system.
Here is the checklist:
- Clear Task Description
- Asset Details
- Priority Level
- Estimated labor and parts
- Assigned technician or team
- Estimated completion time
- The start, due dates, and completion date
- Notes of completion and follow-ups, if there are
If you see, the above points do not miss any of the details that would hamper the work order execution. The most critical among these are the priority level, estimated labor and parts, the data showing follow-ups if those were required, and the technician’s name or the team assigned. These provide confidence to the technicians in executing the work and thereby maintaining compliance, quality, and operational efficiency.
Importance of Work Orders
Today’s CMMS software solutions enable proactive maintenance. These features operate, and their effectiveness depends on the accuracy of maintenance data. The maintenance data further depends on the work order request form. If a task is assigned and executed without any documentation, that is not a work order. Also, the details mentioned in the work order should be accurate and reviewed. The work requests serve data for labor cost reduction, and hence, most organizations across industries are shifting to predictive and preventive maintenance. And this is because preventive maintenance can result in a 20% reduction in equipment downtime, which it does by centralizing asset history and automating schedules. Integrated with Digital Twin, the CMMS software helps them have complete control and visibility of their asset infrastructure and the current status of operational tasks.
Hence, work orders are inevitably important to modern facility management, and they form the heart of maintenance operations.
If you want to further explore the different areas that work orders introduce benefits to, read this blog focused solely on the importance of work orders.
Best Practices to Include in Your Work Order Management

There are types of work order management practices, but here are the key things to include in your customized strategy and existing processes. These include:
Standardizing the field and templates
Before starting to use the CMMS system, the first step is to define a format. If there is no standardized approach to how task descriptions would be created, assets would be tagged, and what technicians should include in notes, everyone will have their own style.
This inconsistent form will fix the failure of the maintenance process even before it has started. Hence, there should be a consistent format that is readable and action-oriented.
Link Work Orders to Asset History
If we see from a technical perspective, the technicians would always perform better when they have the asset history. This gives them detailed insights into the maintenance activities, revealing what happened previously, which parts were affected, which parts were repaired for the moment, but now require a change, etc. This allows them to make data driven decisions, increasing the effectiveness of the process.
This detailed data often reveals the root cause of the issue, which also changes the action to be taken. Hence, your maintenance data should be well-structured without any human error, and the CMMS should be connected to the maintenance history for the technicians to access information readily.
Including photos or attachments
When made a practice, it increases productivity substantially. This includes adding pictures, manuals, or wiring and equipment diagrams when executing service requests.
Automate preventive work orders
Today’s CMMS system is capable of automating work order assignment. This makes the process smoother, ensuring that the accountability is auto-generated by the system. InnoMaint is a system that offers automation routine maintenance, work order management, status update, and closure, allowing organizations to take steps before problems lead to massive failures.
Track Time Cost and Completion
When closing the work order, the maintenance team should review it, considering the following details. These are the time spent on the task by the maintenance staff, the materials used, and if there were deals or follow-ups needed. This helps them refine the process eventually, ensuring quality and regulatory compliance.
Training teams
This practice involves teams knowing the system well, where they will be operating on a daily basis. Organizations should invest in training teams on how to fill out work orders, ensure compliance, report any discrepancies, and treat the service operations in a disciplined way.
Wrapping up
To conclude, the work order management process is an essential feature to optimize maintenance in today’s facility management. It includes maintaining proper formats for work orders/ service tasks, which will further ensure data consistency that is needed for predictive maintenance. Since organizations are aiming for preventative maintenance in 2026, work orders are the heart of maintenance operations across industries.
Frequently Asked Questions
Work order management enables organizations to follow a structured process for their maintenance operation. It is usually done through CMMS software like InnoMaint, which allows advanced work order management systems.
Organizations with poor work order management encounter missed and delayed responses, repeated breakdowns, a lack of accountability, and higher operating costs.
Organizations across sectors use various types of work order management principles, like corrective work orders, preventive work orders, emergency work orders, inspection, and general work orders.
CMMS platforms digitize the complete process, which enables tracking and accountability in real-time. With the use of IoT sensors, the platform reflects real-time data and responses from technicians on-field to assign, track, and measure work orders.
Companies can automate work order management by implementing a CMMS platform that centralizes the entire maintenance workflow. Automation enables auto-creation of work orders from asset schedules, meter readings, or IoT alerts, ensuring issues are captured before failures occur.
The system automatically assigns tasks based on priority, technician availability, and skill sets, while mobile access allows technicians to receive updates, log work, and close tasks in real time. This reduces manual effort, improves response time, and ensures consistent, accountable maintenance operations.




