
Predictive Maintenance Software: The Future of Smart Asset Management in Industry 4.0
The age of reactive maintenance is gradually coming to an end. Businesses can no longer afford to wait for assets to fail. We are in an era defined by real-time data, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT). Organizations are adopting predictive maintenance, a strategic approach.
The predictive maintenance technology has become the backbone of modern asset management, enabling decision-makers to anticipate equipment failures, optimize uptime, and reduce operational costs. Predictive maintenance solutions redefine operational efficiency. They find applications across various industries, including manufacturing plants, energy grids, and transportation hubs. Their usage is becoming inevitable in the digital age.
What is Predictive Maintenance?
Predictive maintenance (PdM) is a proactive maintenance approach that hears the signals from assets. It does so by using IoT sensors, real-time equipment data, and AI-driven analytics. It predicts the likelihood of failure and triggers maintenance schedules dynamically rather than relying on fixed schedules. As predictive maintenance tools monitor the actual equipment condition, they help facility managers make data-backed maintenance decisions at the right time. They analyze vibration, temperature, pressure, and acoustic patterns to figure out warning signs long before breakdowns.
Predictive maintenance empowers business leaders with the information needed to operate assets at peak performance. You can schedule maintenance immediately upon need without having to wait for the turn of static schedules. Predictive maintenance provides the right balance between peak performance and optimal maintenance costs. The technique eliminates the need to overdo preventive maintenance. Predictive maintenance suits large factories where the initial installation costs of predictive maintenance setup are not a matter of concern.
How Predictive Maintenance Software Works?
Predictive maintenance software bridges sensors and assets. It gathers asset condition and performance data continuously. The data flows through IoT gateways into a centralized system integrated with an Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) or Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS) like Innomaint.
This data is fed to machine learning algorithms and AI predictive maintenance models. They promptly identify deviations and anomalies. A CMMS stores and manages data in a way that can be readily accessed, processed, and analysed.
Upon detection of a potential failure, the system automatically triggers alerts and work orders, allowing maintenance teams to intervene at an opportune moment.
The closed feedback loop involving data capture, analysis, prediction and action makes predictive maintenance a powerful part of digital transformation strategies.
Predictive Maintenance vs Preventive Maintenance
Predictive and preventive maintenance both tend to be on the proactive side, but they serve different purposes.
Preventive maintenance is either time-based or usage-based. Maintenance technicians will carry out the tasks repetitively. But sometimes the equipment might not need this task. On the positive side, preventive maintenance ensures maintenance tasks are not ignored for long. But it often leads to unnecessary maintenance and wasted resources.
Unlike preventive maintenance, predictive maintenance relies on real-time data and condition monitoring. It recommends maintenance only when there is actual evidence of wear or impending failure.
| Parameter | Preventive Maintenance | Predictive Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Time or usage-based | Condition-based |
| Data Dependency | Historical | Real-time |
| Cost Efficiency | Moderate | High |
| Downtime Risk | Medium | Low |
| Technology | Basic CMMS scheduling | AI and IoT |
| Outcome | Reduces breakdowns | Prevents approaching failures |
The transition from preventive to predictive maintenance is the need of the hour. It is the transformation from guesswork to certainty.
Key Predictive Maintenance Technologies
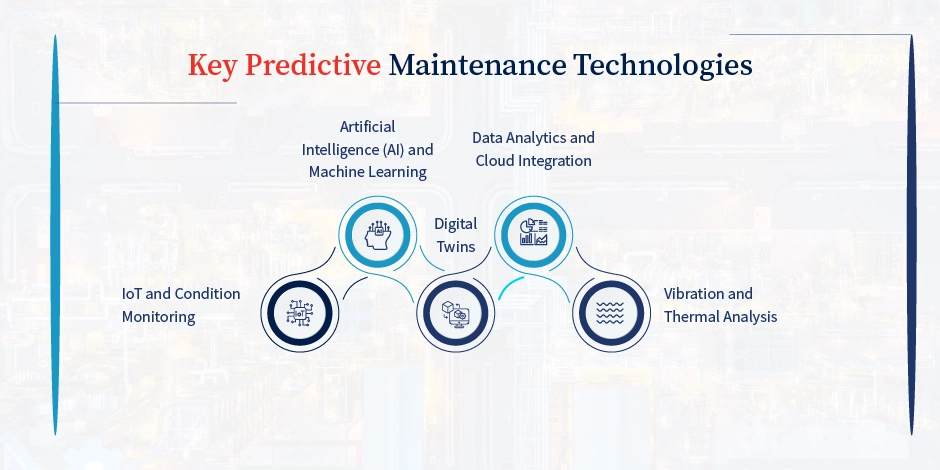
The success of predictive maintenance hinges on several interconnected technologies. Each of these has a say in shaping raw data into actionable insight.
1. IoT and Condition Monitoring
IoT sensors are the frontline components of predictive maintenance. They are miniature devices that track critical parameters such as vibration, temperature, pressure, humidity, etc., in real time. In most cases, the sensors are mounted on equipment. The host assets can send and receive data to and from a central cloud server.
IoT gateway devices can be fitted to both new and old assets. They’ll work perfectly well along with any asset. IoT gateway devices include cameras and microphones that gather and transmit real-time data based on their operational states.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
AI-based predictive maintenance tools learn from historical equipment data and use this knowledge to forecast failures. Machine learning models update their knowledge over time. They improve prediction accuracy with every dataset. This is where Innomaint’s AI for predictive maintenance scores with pattern recognition and anomaly detection capabilities to prevent unplanned downtime.
3. Digital Twins
A digital twin is a virtual replica of a physical asset. It simulates various possible operating conditions. Engineers visualize how an asset might behave under various scenarios and stress. The specialty of Digital Twins is that engineers can obtain the inferences without risking the real equipment. The Digital predictive maintenance capabilities of the Digital Twin find application in sectors like aviation, manufacturing, oil & gas, etc.
4. Data Analytics and Cloud Integration
Predictive maintenance data analytics enables enterprises to think beyond basic monitoring. They can gather, organize, and transform raw data from sensors into useful insights. A correlation is established between equipment performance, standard parameters, historical failure patterns, and real-time anomalies. Maintenance managers can gain a 360-degree view of asset health. Such rich insights entail accurate forecasting, reduce false positives, and most importantly, prioritize the right interventions at the right time. Another remarkable benefit of data analytics is that it reveals trends and new chances for growth that might not be obvious.
Cloud-based predictive maintenance solutions centralize data from multiple industrial units, remote sites, and distributed assets into a single unified environment. This eliminates the practice of working in silos, accelerating maintenance turnaround time. The cloud favors remote diagnostics, collaborative workflows, and seamless integration with ERP, EAM, and CMMS systems. So maintenance teams and supervisors can access updated data and real-time intelligence from anywhere.
5. Vibration and Thermal Analysis
Variations in vibration patterns are early signals of mechanical wear. Vibration analysis for predictive maintenance finds applications in turbines, motors, and compressors.
Benefits of Predictive Maintenance Software
The advantages of predictive maintenance software extend far beyond defeating downtime. Investment in predictive maintenance , in fact, impacts every level of operations for multiple industries. A 2022 Deloitte report quantifies the improvements as below:
- 15% reduction in downtime
- 20% increase in asset productivity
- 30% reduction in inventory levels(as the need for stocking parts that might be rarely required decreases)
Better operational visibility
With increased visibility into field assets and other off-site equipment, OEMs and third-party service providers can deliver greater value.
Optimized costs and performance
Predictive maintenance saves you money and helps you get more use from existing assets. It helps extend asset’s life span.
More empowered teams
As predictive maintenance software forewarns maintenance teams on potential faults, it reduces:
- Instances of breakdowns
- Planned preventive maintenance
- Unplanned downtime
Predictive maintenance solutions empower teams to know exactly how close the equipment is to failure. The use of AI helps forecast future asset operations with greater certainty. This benefit is needed these days, where unpredictable weather, pandemic, and sociopolitical pressures are common.
Reduced Equipment Failures
Predictive maintenance aids in providing a swifter response to problems with its intelligent workflows. Improving the efficiency of maintenance operations increases productivity. There is a significant upshot is improved metrics such as mean time between failures (MTBF),mean time to repair (MTTR), etc.
Optimized Maintenance Costs
Performing maintenance upon needed slashes labor, parts, and service costs. Predictive maintenance can reduce maintenance expenses by up to 30%.
Extended Asset Lifespan
As the predictive maintenance setup monitors assets continuously, maintenance managers can ensure they operate within safe thresholds, reducing avoidable wear and tear.
Reinforces Safety
Predictive maintenance tools help organizations upkeep equipment reliability and uphold safer work environments. They help with regulatory compliance, too!
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
Lesser interventions mean saved energy, too! By preventing over-maintenance, predictive maintenance contributes to lower carbon emissions, thereby aligning with global ESG goals.
Data-Driven Decisions
Predictive maintenance analytics provide a holistic view of equipment performance. Such insights come in handy in better planning, budgeting, and risk management.
How to Implement Predictive Maintenance?
Adopting predictive maintenance into the maintenance workflow isn’t just about deploying technology or installing hardware. It is rather a strategic transformation. It involves the following steps:
1. Define Objectives and Scope
Identify the assets that are mission-critical to your business. Determine the scope of predictive maintenance. Prioritize predictive maintenance techniques for assets whose downtime is relatively costlier or whose failure poses safety risks. Choose the parameter that is to be monitored. Maintenance supervisors must choose this parameter / technique carefully. For example, infrared thermography is best for heat exchangers or electrical panels that tend to leak air or steam. Vibration analysis is recommended for rotating machinery- but not all! There is a nuance here. For equipment rotating slower than 5 rpm, acoustic analysis / oil analysis is preferable over vibration analysis.
2. Deploy IoT Sensors and Set Up Connectivity
Install IoT-based predictive maintenance sensors for real-time asset monitoring. Be careful in choosing the right sensor for the equipment. Integrate them with your Innomaint EAM or CMMS platform for seamless data flow. Ascertain network stability and cybersecurity from the first day, as they are important concerns.
3. Establish Maintenance Protocols
Once the predictive maintenance setup detects and raises alerts on anomalies, formulate automated or semi-automated workflows for responding to alerts. Choose a system that generates maintenance schedules, assigns technicians, and triggers purchase orders, minimizing manual intervention. With the passage of time, predictive algorithms develop into a self-learning maintenance ecosystem.
What are the common predictive maintenance challenges?
The right predictive maintenance strategy shall ensure long-term scalability and success.
Let’s discuss the hurdles in the path to implementing predictive maintenance management system and the ways to conquer them:
i) Data Volume and Quality:
Predictive algorithms are centered on accurate, high-quality historical and real-time data. Data integrity is important for arriving at good predictions. Devise a data governance strategy to ensure consistency and reliability of data.
ii) IoT Device Integration:
Legacy machines are often devoid of digital interfaces. IoT gateways bridge this gap, connecting analog systems to modern predictive maintenance platforms. Emphasize simplifying the connectivity to access any IoT data source without hurdles.
Focus on device security to become immune to cyber-attacks while promoting interoperability across devices. Remember that you may need to scale up in the future. Adopt asset performance management solutions that feature advanced device management and rigid connectivity capabilities. Look for asset performance management solutions that can distill data for non-technical audiences to understand and manipulate.
iii) Algorithm Selection:
Choose the right algorithms matching specific assets to reap success.
iv) Handling change resistance:
It is a usual practice for employees to resist adopting new technologies. Plan and invest in systematic training. Strong leadership skills and transparent communication are vital to navigate the resistance for successful implementation.
v) Initial costs
The startup costs of predictive maintenance infrastructure might be high. But it is justifiable as the investment can be recovered within 6–12 months with reduced downtime and extended asset longevity. The setup costs cover upgrading outdated technology and integrating monitoring systems.
vi) Cybersecurity Risks:
As more assets go online, data protection concerns emerge. Choose predictive maintenance software from companies that offer robust encryption and access controls.
Predictive Maintenance Use Cases Across Industries

Predictive maintenance is transforming nearly every asset-intensive sector. Here’s how it plays out across industries:
1. Manufacturing
In the manufacturing sector, even a short unplanned downtime can cause significant production and supply chain disruptions. Predictive maintenance techniques enable early fault detection for CNC machines to assembly line robots. IoT-based predictive maintenance alerts promote operational continuity and reduce scrap rates.
2. Energy and Utilities
In the energy sector, predictive maintenance tools can be used to monitor turbines, transformers, and substations. Predictive maintenance analytics can uncover blade imbalances and gearbox wear, preventing catastrophic failures.
3. Transportation and Rail
Predictive maintenance analytics indicate rail track deformations, void formation, and brake issues in advance. The IoT-driven analytics improve passenger safety and extend the life of rail infrastructure.
4. Oil and Gas
The process of oil drilling makes the assets weary. The sudden failure of assets can be dangerous. Predictive maintenance helps monitor oil temperature, gearboxes in drilling equipment. You can integrate vibration analysis and thermal sensors. The timely alerts help operators avert leakages, unplanned shutdowns, and save maintenance costs by up to 40%.
5. Aviation
Aircraft predictive maintenance uses digital twins and AI to forecast failures in engines, landing gear, and avionics. Airlines bank on PdM to reinforce safety, reduce delays, and optimize maintenance schedules.
6. Automotive and Heavy Equipment
Automotive manufacturers use AI predictive maintenance to analyze sensor data from robots and conveyor systems. Predictive maintenance helps automobile manufacturers monitor spot-welding guns that do 15,000 welds in a day. The hints on nearing failures minimize the failure of these assets and enhance quality assurance.
The Future of Predictive Maintenance
The convergence of AI, IoT, and digital twins marks the future of predictive maintenance. The interconnected ecosystem predicts, prescribes, and prevents failures as per Industry 4.0 principles.
The emerging trends include:
* AI-powered root cause analysis that provides recommendations in addition to the detection of approaching failures.
* Edge computing, for faster data processing near the asset itself.
* Integration of Industry 4.0 predictive maintenance, integrating with ERP and supply chain management systems for end-to-end visibility.
* Sustainability analytics, linking maintenance performance to ESG metrics.
* Digital twin predictive maintenance combined with augmented reality for technician training and visualization.
Whether you operate in manufacturing, automobile, energy, or oil & gas sectors, Innomaint helps you suppress and stay ahead of equipment failures. You thus ensure every asset performs at peak efficiency. Monitor asset health data live from a centralized location with enterprise-wide visibility. Achieve measurable ROI through reduced downtime and lower maintenance costs. Keep assets healthy, costs low, and productivity high by choosing Innomaint.
Frequently Asked Questions
Predictive maintenance software is a maintenance management solution that uses real time sensor data, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and AI driven analytics to forecast when equipment is likely to fail. Instead of relying on fixed schedules, it monitors actual asset condition, detects early warning signs such as abnormal vibration or temperature, and recommends interventions only when they are really needed.
Predictive maintenance software continuously collects condition and performance data from assets through IoT sensors and gateways. This data flows into a central platform, often integrated with an Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) or Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS), where AI and machine learning models analyze patterns and anomalies. When the software detects a potential failure, it automatically triggers alerts and work orders so maintenance teams can intervene at the most opportune time.
Preventive maintenance is time or usage based and follows predefined schedules, regardless of the asset’s real condition, which can sometimes lead to unnecessary work. Predictive maintenance is condition based and uses real time data from sensors to identify actual signs of wear or impending failure, so teams perform maintenance only when there is clear evidence that it is needed. This reduces wasted effort, minimizes downtime risk, and improves cost efficiency compared with purely schedule driven maintenance.
Predictive maintenance software helps organizations reduce unplanned downtime, extend asset lifespan, and optimize maintenance costs. By acting before failures occur, it improves key performance metrics such as mean time between failures (MTBF) and mean time to repair (MTTR), lowers spare parts inventory requirements, and reduces the need for over maintenance. It also enhances safety, supports regulatory compliance, improves energy efficiency, and gives decision makers better visibility for planning and budgeting.
Any asset intensive industry can benefit from predictive maintenance software, including manufacturing, energy and utilities, transportation and rail, oil and gas, aviation, and automotive and heavy equipment. In these sectors, IoT based condition monitoring and predictive analytics help detect early faults in turbines, transformers, CNC machines, robots, drilling equipment, and rail or aviation assets, preventing costly disruptions and improving service quality.
To implement predictive maintenance, organizations should first define clear objectives and identify critical assets where downtime is most costly or risky. They then deploy appropriate IoT sensors and connectivity, integrate data streams with an EAM or CMMS platform, and configure AI or analytics models to monitor key parameters. Finally, they set up automated workflows that convert alerts into work orders, assign technicians, and trigger purchases so that insights from the predictive system translate into timely maintenance actions.
Common challenges include handling large volumes of sensor data, ensuring data quality, integrating IoT devices with legacy equipment, and selecting the right algorithms for different assets. Organizations also face change management issues when teams resist new ways of working, as well as high initial setup costs for sensors, gateways, and connectivity. Cybersecurity is another key concern because more connected assets mean more potential entry points for attacks, so strong encryption and access controls are essential.
Many organizations recover their initial investment in predictive maintenance within 6 to 12 months, thanks to reduced downtime, fewer breakdowns, and lower maintenance and inventory costs. Industry studies show that predictive maintenance can cut downtime by around 15 percent, increase asset productivity by about 20 percent, and reduce inventory levels by roughly 30 percent, which all contribute to a strong and measurable return on investment.
Predictive maintenance was initially adopted by large factories and asset heavy enterprises because of the upfront cost of sensors and infrastructure, but modern cloud based platforms and modular IoT solutions have made it more accessible for mid sized businesses too. Companies can start with a limited scope by monitoring their most critical assets, prove value, and then scale gradually as savings from reduced downtime and extended asset life fund further investment.




